800.676.5565 | info@jantdx.com

RAMP NT-proBNP Test
The FDA cleared whole blood immunoassay RAMP NT-proBNP test detects the levels of N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with congestive heart failure.
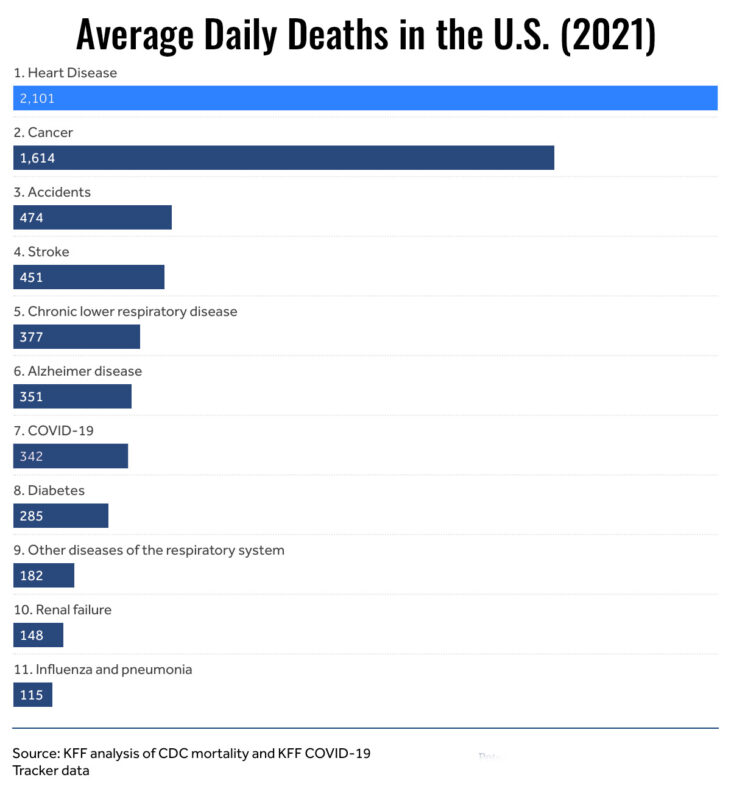
Heart Disease is the Leading Cause of Death
According to CDC data, heart disease is the leading cause of death for people of most racial and ethnic groups in the United States. High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease.¹
Nearly 1 in 4 heart failure (HF) patients are readmitted within 30 days of discharge and approximately half are readmitted within 6 months.²
Heart disease is the most expensive condition to treat.³
The first step to saving lives by preventing heart disease fatalities is more comprehensive cardiac testing.
What are the advantages of NT-proBNP?
Heart failure (HF) often presents with non-specific symptoms and is frequently confused with pneumonia or COPD.
Most HF patients are treated with traditional medication that disrupts BNP levels, but NT-proBNP will not be affected. These increased BNP levels often lead to misinterpretations in the response of patients after treatment.
As the plasma levels of NT-proBNP are not affected by the medication, thus NT-proBNP is a more accurate natriuretic biomarker than BNP for HF diagnosis and prognosis.
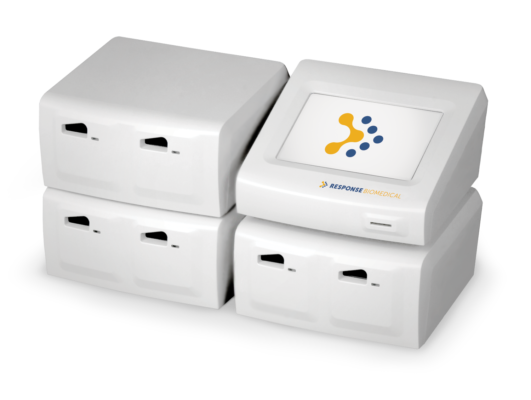


Quantitative test for determination of NT-proBNP in EDTA whole blood
References:
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, October 14). Heart disease facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm
2. Khan, M. S., & Al, E. (2021, April 19). Trends in 30- and 90-day readmission rates for heart failure. Circulation: Heart Failure. Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008335
3. Five most expensive diseases. NABR.ORG. (n.d.). Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://www.nabr.org/biomedical-research/importance-biomedical-research/five-most-expensive-diseases
4. Panagopoulou, V., Deftereos, S., Kossyvakis, C., Raisakis, K., Giannopoulos, G., Bouras, G., Pyrgakis, V., & W.Cleman, M. (2013). NTproBNP: An Important Biomarker in Cardiac Diseases. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 13(2), 82–94. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026611313020002
5. Pro-Brain natriuretic peptide (Pro-BNP), plasma. Quest Joint DOS. (n.d.). Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://jdos.nicholsinstitute.com/dos/sarasotamemorial/test/116766
6. Lüers C;Schmidt A;Wachter R;Fritzsche F;Sutcliffe A;Kleta S;Zapf A;Hagenah G;Binder L;Maisch B;Pieske B; (2010, October). Serial NT-probnp measurements for risk stratification of patients with decompensated heart failure. Herz. Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20927502
7. Lee-Lewandrowski E;Januzzi JL;Green SM;Tannous B;Wu AH;Smith A;Wong A;Murakami MM;Kaczmarek J;Apple FS;Miller WL;Hartman K;Jaffe AS;, E. (2007, July 25). Multi-center validation of the Response Biomedical Corporation ramp NT-probnp assay with comparison to the roche diagnostics gmbh elecsys probnp assay. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry. Retrieved December 7, 2022, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17854790